In modern implant dentistry, Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) is a game-changing technology. With unmatched 3D imaging capabilities, CBCT empowers dentists to diagnose, plan, and execute implant procedures with higher precision and safety.
This article explores how CBCT elevates implantology and how to harness its full potential in your daily practice.
What is CBCT?
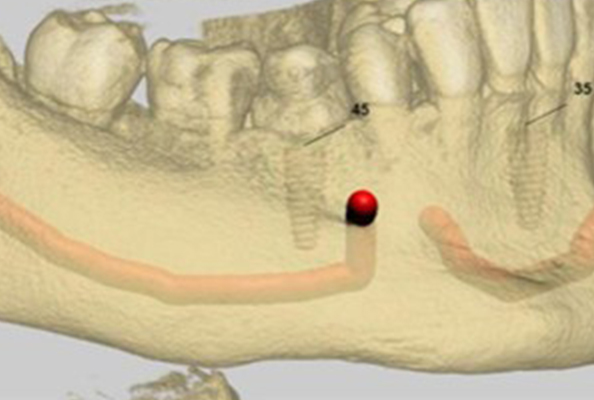
CBCT is a 3D imaging technique that provides high-resolution scans of the oral and maxillofacial region. Unlike 2D radiographs, CBCT captures bone structure, soft tissue, and critical anatomical landmarks from every angle—offering a complete view of the patient’s anatomy for safer and more predictable implant planning.
Why CBCT Matters in Implantology
1. Improved Diagnostic Accuracy
CBCT enables visualization of:
- Bone density and volume
- Nerve pathways (e.g., inferior alveolar nerve)
- Sinus positioning and variations
- Bone resorption or defects
Key takeaway: Early, accurate diagnostics reduce surgical surprises and improve case selection.
2. Precise Implant Placement
CBCT allows for:
- Accurate measurements of available bone
- Selection of ideal implant size, angulation, and depth
- Avoidance of anatomic risks
Key takeaway: With CBCT, implants are placed exactly where they should be—improving stability and longevity.
3. Virtual Treatment Planning
With CBCT software, you can:
- Simulate implant placement on a 3D model
- Adjust positioning in a digital environment
- Account for bone quality, prosthetic space, and neighboring structures
Key takeaway: Pre-planning digitally increases precision and reduces intraoperative stress.
4. Guided Implant Surgery
CBCT data can be used to create custom surgical guides, which translate virtual planning into exact real-world positioning.
Benefits include:
- Shorter surgical time
- Minimized trauma
- Enhanced esthetic and functional outcomes
Key takeaway: Guided surgery turns planning into predictable reality.
5. Reduced Surgical Risks
CBCT helps prevent:
- Nerve damage
- Sinus perforation
- Malpositioning or implant failure
Key takeaway: Clear visualization minimizes complications.
6. Post-Operative Assessment
After implant placement, CBCT allows you to:
- Monitor healing
- Detect early signs of failure or peri-implantitis
- Evaluate bone integration
Key takeaway: Follow-up CBCT ensures timely intervention if needed.
How to Maximize CBCT in Implantology
1. Make CBCT a Standard Protocol
Use CBCT for every implant case, not just complex ones. It ensures:
- No anatomic details are missed
- All cases benefit from enhanced planning and safety
2. Invest in Quality Software and Training
Equip your team with:
- Advanced planning software (with guide creation and 3D overlay tools)
- Ongoing training in image interpretation and treatment simulation
Tip: The right tools—and knowing how to use them—are critical to maximizing your investment.
3. Use CBCT to Assess Bone Quality
CBCT helps determine if:
- Bone grafting is needed
- Implant size or type needs adjustment
- Sites are suitable for immediate or delayed loading
Tip: Match the implant to the bone—not the other way around.
4. Use 3D Visualization to Educate Patients
CBCT enhances patient trust and case acceptance by:
- Showing 3D images of their anatomy
- Explaining risks and benefits clearly
- Demonstrating the treatment plan visually
5. Integrate CBCT with Other Digital Tools
Combine CBCT with:
- Intraoral scanning
- CAD/CAM systems
- Digital lab communication
Tip: A fully integrated digital workflow boosts speed, accuracy, and consistency.
Conclusion
CBCT is not just another diagnostic tool—it’s the foundation of precision-driven implantology. When fully utilized, it allows for:
- Smarter treatment planning
- Safer, more accurate implant placement
- Better long-term results
Whether you’re new to CBCT or looking to deepen your integration, now is the time to make it a core part of your workflow. The future of implant dentistry is digital, and CBCT is at its center.